THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM - Info Dear
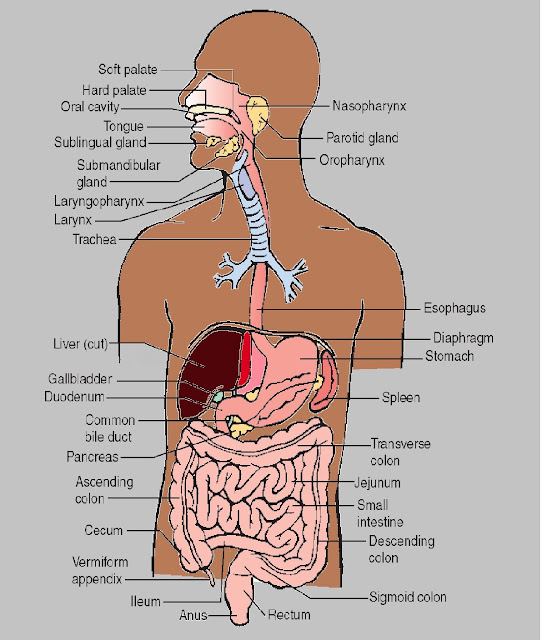
THE HUMAN DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
Introduction:-
Animal required water, oxygen, simple sugar, amino acids, fatty acids, vitamins and many other inorganic and organic substances. These substances except water and oxygen are rare in the natural environment and are not directly available to the organisms. In nature, these substances are available in the form of fats, protein, starch, vitamin, and minerals. In these substances, vitamin and minerals are not able to use without break down and digested into simple molecules such as amino acid, sugars and fatty acid for that purpose animals have a specific system to digest complex molecules into simple molecules called The Digestive System.
Digestive System Function
Digestion in Buccal Cavity OR Digestion in Mouth/ Oral Cavity:-
There are three functions of the oral cavity in digestion.
(i) Selection of food
(ii) Grinding or Mastication
(iii) Lubrication and digestion
Selection of food:-
When the food enters the oral cavity. It is tasted, smelled and felt if the taste or smell is unpleasant or the food contains any hard object like boner or dirt present in the food then the food is rejected by the tongue.
Tongue:-
Tongue acts as the sensory and muscular organ and plays an important role in the selection of food with the help of its taste buds.
Grinding or Mastication:-
After the selection of food particles, the food ground into small pieces by molar teeth this is very useful because of two reasons
(i) The esophagus allows relatively small pieces to pass through it.
(ii) Small pieces have much surface for the enzyme to attach.
The Human Teeth
The grinding process is performed by the teeth there are the teeth types present in human.
Incisors:-
These are the front teeth that grow after our primary teeth or baby teeth. Incisors are used to catch anything with a mouth. Incisors make our smiles more beautiful.
Canines:-
These are the teeth present just after the incisors. These teeth are relatively large in size than the other teeth. These are sharpening than the other teeth. These are stronger than incisors.
Premolars:-
These are the transitional teeth present between the canine and molar teeth. There are four premolar teeth in the upper jaw and four premolar teeth in the lower jaw that make eight premolar teeth in human teeth set.
Molars:-
These are the teeth present at the back of the mouth. These are large, flat teeth commonly used in the primarily grinding of food during the chewing process.
Wisdom Teeth:-
These are the last teeth in the human mouth. These are also known as the 3rd molar. These teeth usually break the gum tissue and grow causing pain after the age of 17. Sometimes wisdom teeth stay completely buried under the gum tissue.
Lubrication and digestion:-
Three pairs of glands named
(i) Sublingual glands (situated below the tongue).
(ii) Submaxillary glands (situated behind the jaws)
(iii) Parotid Gland (situated in front of the ears)
The saliva produced by these glands contains the following ingredients
Water and Mucus:-
Water and mucus make together a slimy liquid which serves to lubricate the food which increases the chewing efficiency and food passed the esophagus smoothly.
Sodium bicarbonate and some other salts:-
Sodium bicarbonate and some other salts are slightly antiseptic (act against the pathogens). But their main function is to stabilize the Ph (power of Hydrogen atom) of the food.
Amylase or Ptyalin:-
Amylase or ptyalin is an enzyme that digests carbohydrate that mixed in food to the digest starch and glycogen into maltose.
Swallowing Process:-
As a result of mastication, the slimy food forms an oval lump structure called bolus. Then bolus is pushed to back of mouth by the action of the tongue and muscles of the pharynx which prevents the food “bolus” to enter in the windpipe (trachea). There are the following steps occur during the swallowing process.
(a) The tongue moves upwards and backward against the roof of the mouth, forcing the bolus to the back of the mouth cavity.
(b) The backward movement of the tongue pushes the soft plates up and closes the nasal opening at the back. At the same time, the tongue forces the epiglottis (a flap of cartilage) into more or less horizontal position these closing the opening of the windpipe (the glottis)
(c) The larynx, cartilage around the top of the windpipe, moves upward under the back of the tongue.
(d) The glottis is partly closed by the contraction of a ring of muscle.
(e) The food does not enter partly open glottis because the epiglottis diverts the bolus to one side of the opening and safely down the esophagus.
(f) The beginning of the swallowing action is voluntary but once the food reaches the back of the mouth, swallowing becomes automatic. Then food is forced downward by a specific movement of the esophagus.
Esophagus:-
The esophagus is a muscular tube that provides the pathway to food from the throat (pharynx) to the stomach. Esophagus contains a moist tissue called mucosa. The esophagus is about 8 inches long and present in front of the spine and behind the windpipe (trachea) and the heart.
Peristalsis:-
The specific movement of the digestive tract by which food moves in the digestive canal. It consists of two types of muscles circular and longitudinal muscles these muscles form a specific wave of movement for food which forces the food to move in the digestive canal (Gut). This peristalsis movement starts from behind the Buccal cavity along the esophagus to the stomach and then along the whole digestive tract.
Antiperistalsis:-
The reversed movement of the digestive tract is called antiperistalsis. Which cause the backward movement of food such as the food passed from intestine back into the stomach and even into the mouth and leading to vomiting.
Hunger Pang:-
Hunger contractions are also called peristalsis contraction which is increased by low blood glucose levels and are sufficiently strong to create an uncomfortable sensation which is known as hunger pang. It usually begins 12 to 24 hour after the previous meal or in less time for some people.
Digestion In Stomach
Cardiac Sphincter:-
At the place where esophagus and stomach are joined each other a valve called cardiac sphincter made up of a special ring of muscles. When the food enters the stomach then this valve prevents the contents of the stomach from moving back into the esophagus. It opens when the peristalsis coming toward the stomach.
Heart Burn OR Pyrosis:-
It is a painful burning sensation in the chest usually associated with the backflush of the acidic chime (partly digest food of stomach) into the esophagus. This is due to overeating fatty food, laying down immediately after a meal, consuming too much alcohol, caffeine or smoking.